Allergy Safety • Preparedness • Travel • Free Alert Cards • Support Groups
EpiPen Resources Guide
Aggregated, practical guidance authority websites, storage, expiration dates, disposal, FDA approved alternatives and More…
Educational information only — always follow your clinician’s guidance and your personalized action plan.


EpiPen and anaphylaxis experts
Manufacturer and school sites for training

How epinephrine works
When to give it
Why you should carry two

Avoid extreme heat and freezing
Don’t leave it in a car
Store where you can reach it fast

Expired! Are they safe?
Enter expiration on calendar
Refill early (don’t wait for the last week)
Are sharps
Classified as acute hazardous waste
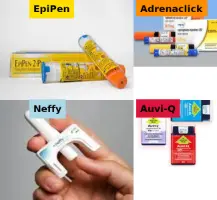
Epinephrine auto-injector products
EpiPen resource hub aggregates trusted guidance on recognizing anaphylaxis, when and how to use epinephrine, safe storage and expiration, disposal, FDA-approved alternatives, and flashcards for quick recall. It links to expert sites and practical topics, and includes FAQs focused on real user concerns. The page emphasizes immediate epinephrine use for severe reactions, calling emergency services, and carrying two auto-injectors, and frames everything as educational, not medical advice.
Everything here is free. We’re a mission-driven hub, not a commercial site.
Nothing here replaces medical advice—always work with your doctor to create a personalized allergy action plan.
Flashcards
Fast, high-retention summaries for food-allergy safety. Also known as Cheat Sheets
Epinephrine first
30 sec- Use epinephrine at first concern
- Antihistamines don't work.
- Seconds matter.
Breathing or Fainting = Emergency
Urgent- Trouble breathing, swelling, collapse.
- Treat as anaphylaxis.
- Act immediately—don’t wait.
When in doubt, treat
First-line- It’s safer to treat early than late.
- Follow your action plan..
- Get emergency help after
Call for Help After
Always- Call emergency services after epinephrine.
- Tell them “anaphylaxis
- Stay under medical monitoring
Position Matters
Hidden risk- If dizzy/faint: lay flat, raise legs.
- Don’t stand or walk.
- Sit up only if breathing is hard
Carry two auto-injectors
Plan- Carry two auto-injectors.
- A second dose may be needed.
- Know where EpiPen are.